IoT Connectivity: The Backbone of a Smarter World
IoT connectivity refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data with each other via the internet. This seamless communication allows for automation, monitoring, and control of various systems and processes. Imagine your coffee maker chatting with your smartphone to brew coffee just as you wake up! That’s IoT in action.
The Evolution of IoT
IoT has grown from its early iterations of basic machine-to-machine communication to a complex ecosystem. It now includes billions of devices, increasing global connectivity beyond all previous levels. From simple sensors to sophisticated smart systems, the transition has been nothing short of transformative.
Core Components of IoT Connectivity
Sensors and Actuators
Sensors collect data from the environment, such as temperature, humidity, or motion. Actuators, on the other hand, are devices that take actions based on the data received from sensors, like turning on a fan when the temperature rises.
Communication Protocols
Protocols define how devices communicate. Common protocols include MQTT for lightweight messaging and HTTP for web-based communication.
Data Storage and Processing
IoT generates vast amounts of data, necessitating robust storage and processing solutions. Cloud computing and edge computing play crucial roles in managing and analyzing this data.
Types of IoT Networks
Personal Area Networks (PAN)
PANs are short-range networks, typically used for connecting personal devices like smartphones and wearables.
Local Area Networks (LAN)
LANs cover a small geographic area, such as a home or office, connecting devices like computers and printers.
Wide Area Networks (WAN)
WANs cover large geographic areas, connecting multiple LANs. The internet itself is the largest WAN.
Key Technologies in IoT Connectivity
Ethernet and Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi and Ethernet are the most common technologies for IoT connectivity. Wi-Fi offers flexibility, while Ethernet provides reliable, high-speed connectivity.
Cellular Networks (4G, 5G)
Cellular networks enable IoT devices to communicate over long distances. 5G technology promises faster speeds and lower latency, enhancing IoT applications.
Low-Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN)
LPWANs are designed for long-range communication with low power consumption, making them ideal for IoT applications like smart meters and agriculture.
Bluetooth and Zigbee
Bluetooth is great for short-range communication, while Zigbee is used for low-power, low-data-rate applications in home automation.
IoT Protocols and Standards
MQTT and CoAP
MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol ideal for low-bandwidth, high-latency networks. CoAP is designed for constrained nodes and networks.
HTTP/HTTPS
HTTP/HTTPS is widely used for web-based communication, ensuring secure data transmission over the internet.
Zigbee and Z-Wave
Zigbee and Z-Wave are popular for home automation, providing reliable, low-power communication for smart devices.
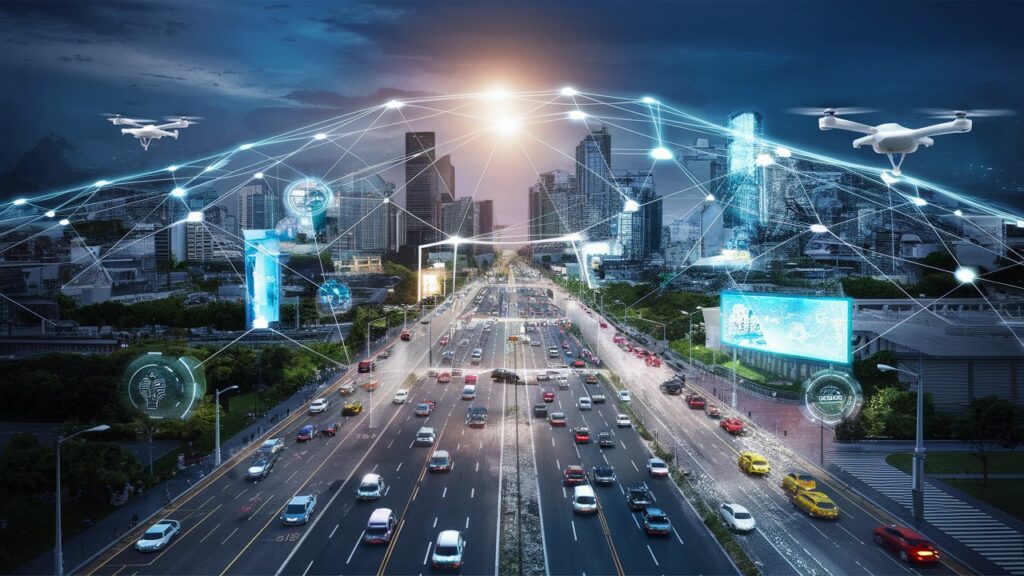
Applications of IoT Connectivity

Smart Homes
Smart homes use IoT connectivity to automate lighting, heating, and security systems, enhancing comfort and energy efficiency.
Healthcare and Wearables
IoT in healthcare enables remote monitoring of patients, improving healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
IIoT leverages IoT connectivity to enhance manufacturing processes, predictive maintenance, and supply chain management.
Smart Cities
Smart cities use IoT to improve public services, traffic management, and energy consumption, making urban living more efficient.
Agriculture and Farming
IoT applications in agriculture include smart irrigation systems, livestock monitoring, and crop health management, boosting productivity and sustainability.
Challenges in IoT Connectivity
Security Concerns
With more devices connected, security becomes a major concern. Ensuring data privacy and protecting against cyber threats are crucial.
Scalability Issues
As the number of IoT devices grows, scaling networks to handle the increased load without compromising performance is challenging.
Interoperability Challenges
Different devices and platforms often use various protocols and standards, making seamless interoperability a significant challenge.
Future Trends in IoT Connectivity
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
AI and ML will enhance IoT applications by enabling predictive analytics, automation, and intelligent decision-making.
Edge Computing
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the data source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage.
6G Technology
The next generation of wireless technology, 6G, promises even faster speeds, greater bandwidth, and more reliable connectivity for IoT devices.
Impact of IoT Connectivity on Various Industries
Manufacturing
IoT connectivity drives Industry 4.0, revolutionizing manufacturing with automation, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance.
Healthcare
The IoT improves patient care with remote monitoring, wearable health devices, and smart medical equipment, enhancing diagnosis and treatment.
Transportation
Smart transportation systems use IoT to optimize traffic flow, improve vehicle safety, and enhance public transportation services.
Agriculture
The IoT in agriculture enhances farming practices through smart irrigation, soil monitoring, and livestock tracking, increasing yields and sustainability.
Retail
Retailers use IoT for inventory management, customer tracking, and personalized shopping experiences, boosting efficiency and sales.
Case Studies: Successful IoT Implementations
Smart Homes: The Rise of Home Automation
From voice-activated assistants to smart thermostats, smart homes are making life more convenient and energy-efficient.
Healthcare: Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote monitoring systems allow healthcare providers to track patient vitals in real time, reducing hospital visits and improving patient outcomes.
Industrial IoT: Predictive Maintenance
Industrial IoT uses sensors and data analytics to predict equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
How to Get Started with IoT Connectivity
Choosing the Right Devices
Selecting compatible and reliable devices is crucial. Consider factors like connectivity options, power consumption, and scalability.
Setting Up an IoT Network
A well-designed network is essential. Start with a robust infrastructure, ensuring secure and reliable connectivity across all devices.
Developing IoT Applications
Develop applications tailored to your needs. Focus on user experience, data analytics, and seamless integration with other systems.
Regulations and Compliance in IoT Connectivity
Data Privacy Laws
Compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR is essential to protect user data and avoid legal repercussions.
Industry Standards and Certifications
Adhering to industry standards and obtaining relevant certifications ensures IoT devices’ interoperability, security, and reliability.
The Role of Cloud Computing in IoT
Benefits of Cloud Integration
Cloud computing offers scalable storage and processing power, enabling real-time data analysis and remote management of IoT devices.
Popular IoT Cloud Platforms
Platforms like AWS IoT, Microsoft Azure IoT, and Google Cloud IoT provide comprehensive solutions for managing IoT devices and data.
Security Best Practices for IoT Connectivity
Encrypting Data
Encrypt all data transmitted between devices to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Implementing Strong Authentication
Use strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication, to ensure that only authorized users can access the network.
Regular Security Audits
Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in your IoT infrastructure.
The Future of IoT Connectivity
The future of IoT connectivity is bright, with technological advancements promising even more seamless and intelligent interactions between devices. As we continue to innovate, IoT will undoubtedly transform our lives in ways we can only imagine.
Final Thoughts
IoT connectivity is not just a technological trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how we interact with the world around us. By understanding its components, applications, and challenges, we can harness its potential to create a smarter, more connected world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is IoT Connectivity?
IoT connectivity refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data via the Internet, enabling automation and remote control.
2. How does IoT impact everyday life?
IoT enhances everyday life by automating tasks, improving efficiency, and enabling smart applications like home automation, healthcare monitoring, and smart cities.
3. What are the main challenges in IoT Connectivity?
The main challenges include security concerns, scalability issues, and interoperability between different devices and platforms.
4. What is the role of cloud computing in IoT?
Cloud computing provides scalable storage and processing power, enabling real-time data analysis and remote management of IoT devices.
5. How can I ensure the security of my IoT devices?
Ensure the security of IoT devices by encrypting data, implementing strong authentication methods, and conducting regular security audits.














Post Comment